Linux查看磁盘、文件系统、文件夹、文件大小的命令(lsblk、df、du、ll) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › linux 查看目录大小排序 › Linux查看磁盘、文件系统、文件夹、文件大小的命令(lsblk、df、du、ll) |
Linux查看磁盘、文件系统、文件夹、文件大小的命令(lsblk、df、du、ll)
|
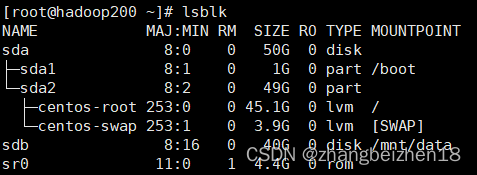
记录:325 场景:在CentOS 7.9操作系统上,使用lsblk命令查看磁盘大小和磁盘挂载情况;使用df查看文件系统大小和挂载情况;使用du命令查看文件夹(目录)大小;使用ll和ls查看文件大小。 版本: 操作系统:CentOS 7.9 1.lsblk常用命令 (1)帮助命令 命令:lsblk --help 功能:查看lsblk支持全部命令和选项,在实际工作中,查看这个手册应该是必备之选。 (2)查看磁盘大小 命令:lsblk 命令:lsblk -a 功能:查看挂载磁盘信息,磁盘名称、大小、挂载目录等。
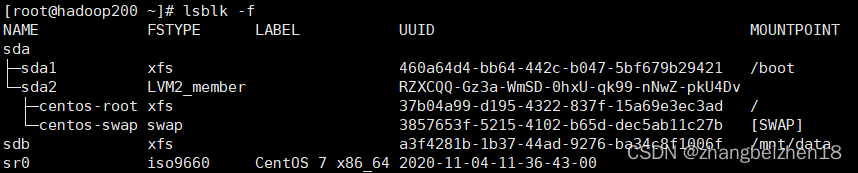
(2)查看磁盘文件系统信息 命令:lsblk -f 功能:查看挂载磁盘信息,磁盘名称、文件系统类型、UUID、挂载目录等。
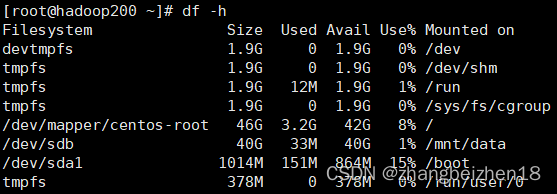
2.df常用命令 (1)帮助命令 命令:df --help 功能:查看df支持全部命令和选项,在实际工作中,查看这个手册应该是必备之选。 (2)查看文件系统大小 命令:df -h 功能:查看文件系统信息,文件系统总容量、已用容量、可用容量、挂载目录等。
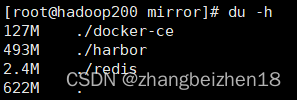
3.du常用命令 (1)帮助命令 命令:du --help 功能:查看du支持全部命令和选项,在实际工作中,查看这个手册应该是必备之选。 (2)查看文件夹(目录)大小 命令:du -h 功能:查看文件夹(目录)大小。
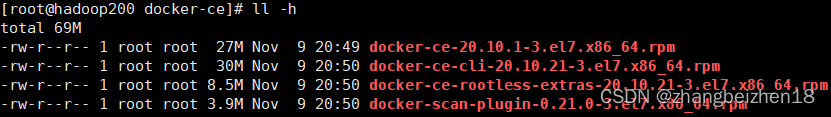
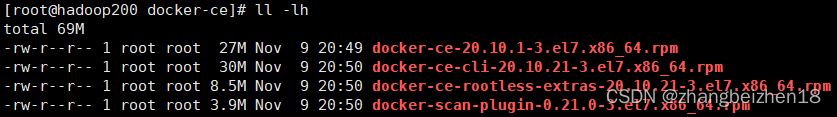
4.ll常用命令 (1)帮助命令 命令:ll --help 功能:查看ll支持全部命令和选项,在实际工作中,查看这个手册应该是必备之选。 (2)查看文件夹(目录)大小 命令:ll -h 功能:查看文件大小。
5.ls常用命令 (1)帮助命令 命令:ls --help 功能:查看ls支持全部命令和选项,在实际工作中,查看这个手册应该是必备之选。 (2)查看文件夹(目录)大小 命令:ls -lh 功能:查看文件大小。
6.命令和选项 6.1 lsblk命令 执行命令:lsblk --help,查看详细帮助手册。 Usage: lsblk [options] [ ...] Options: -a, --all print all devices -b, --bytes print SIZE in bytes rather than in human readable format -d, --nodeps don't print slaves or holders -D, --discard print discard capabilities -e, --exclude exclude devices by major number (default: RAM disks) -I, --include show only devices with specified major numbers -f, --fs output info about filesystems -h, --help usage information (this) -i, --ascii use ascii characters only -m, --perms output info about permissions -l, --list use list format output -n, --noheadings don't print headings -o, --output output columns -p, --paths print complate device path -P, --pairs use key="value" output format -r, --raw use raw output format -s, --inverse inverse dependencies -t, --topology output info about topology -S, --scsi output info about SCSI devices -h, --help display this help and exit -V, --version output version information and exit Available columns (for --output): NAME device name KNAME internal kernel device name MAJ:MIN major:minor device number FSTYPE filesystem type MOUNTPOINT where the device is mounted LABEL filesystem LABEL UUID filesystem UUID PARTLABEL partition LABEL PARTUUID partition UUID RA read-ahead of the device RO read-only device RM removable device MODEL device identifier SERIAL disk serial number SIZE size of the device STATE state of the device OWNER user name GROUP group name MODE device node permissions ALIGNMENT alignment offset MIN-IO minimum I/O size OPT-IO optimal I/O size PHY-SEC physical sector size LOG-SEC logical sector size ROTA rotational device SCHED I/O scheduler name RQ-SIZE request queue size TYPE device type DISC-ALN discard alignment offset DISC-GRAN discard granularity DISC-MAX discard max bytes DISC-ZERO discard zeroes data WSAME write same max bytes WWN unique storage identifier RAND adds randomness PKNAME internal parent kernel device name HCTL Host:Channel:Target:Lun for SCSI TRAN device transport type REV device revision VENDOR device vendor For more details see lsblk(8).6.2 df命令 执行命令:df --help,查看详细帮助手册。 Usage: df [OPTION]... [FILE]... Show information about the file system on which each FILE resides, or all file systems by default. Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too. -a, --all include pseudo, duplicate, inaccessible file systems -B, --block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g., '-BM' prints sizes in units of 1,048,576 bytes; see SIZE format below --direct show statistics for a file instead of mount point --total produce a grand total -h, --human-readable print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G) -H, --si likewise, but use powers of 1000 not 1024 -i, --inodes list inode information instead of block usage -k like --block-size=1K -l, --local limit listing to local file systems --no-sync do not invoke sync before getting usage info (default) --output[=FIELD_LIST] use the output format defined by FIELD_LIST, or print all fields if FIELD_LIST is omitted. -P, --portability use the POSIX output format --sync invoke sync before getting usage info -t, --type=TYPE limit listing to file systems of type TYPE -T, --print-type print file system type -x, --exclude-type=TYPE limit listing to file systems not of type TYPE -v (ignored) --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit Display values are in units of the first available SIZE from --block-size, and the DF_BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE and BLOCKSIZE environment variables. Otherwise, units default to 1024 bytes (or 512 if POSIXLY_CORRECT is set). SIZE is an integer and optional unit (example: 10M is 10*1024*1024). Units are K, M, G, T, P, E, Z, Y (powers of 1024) or KB, MB, ... (powers of 1000). FIELD_LIST is a comma-separated list of columns to be included. Valid field names are: 'source', 'fstype', 'itotal', 'iused', 'iavail', 'ipcent', 'size', 'used', 'avail', 'pcent', 'file' and 'target' (see info page). GNU coreutils online help: For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'df invocation'6.3 du命令 执行命令:du --help,查看详细帮助手册。 Usage: du [OPTION]... [FILE]... or: du [OPTION]... --files0-from=F Summarize disk usage of each FILE, recursively for directories. Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too. -0, --null end each output line with 0 byte rather than newline -a, --all write counts for all files, not just directories --apparent-size print apparent sizes, rather than disk usage; although the apparent size is usually smaller, it may be larger due to holes in ('sparse') files, internal fragmentation, indirect blocks, and the like -B, --block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g., '-BM' prints sizes in units of 1,048,576 bytes; see SIZE format below -b, --bytes equivalent to '--apparent-size --block-size=1' -c, --total produce a grand total -D, --dereference-args dereference only symlinks that are listed on the command line -d, --max-depth=N print the total for a directory (or file, with --all) only if it is N or fewer levels below the command line argument; --max-depth=0 is the same as --summarize --files0-from=F summarize disk usage of the NUL-terminated file names specified in file F; if F is -, then read names from standard input -H equivalent to --dereference-args (-D) -h, --human-readable print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G) --inodes list inode usage information instead of block usage -k like --block-size=1K -L, --dereference dereference all symbolic links -l, --count-links count sizes many times if hard linked -m like --block-size=1M -P, --no-dereference don't follow any symbolic links (this is the default) -S, --separate-dirs for directories do not include size of subdirectories --si like -h, but use powers of 1000 not 1024 -s, --summarize display only a total for each argument -t, --threshold=SIZE exclude entries smaller than SIZE if positive, or entries greater than SIZE if negative --time show time of the last modification of any file in the directory, or any of its subdirectories --time=WORD show time as WORD instead of modification time: atime, access, use, ctime or status --time-style=STYLE show times using STYLE, which can be: full-iso, long-iso, iso, or +FORMAT; FORMAT is interpreted like in 'date' -X, --exclude-from=FILE exclude files that match any pattern in FILE --exclude=PATTERN exclude files that match PATTERN -x, --one-file-system skip directories on different file systems --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit Display values are in units of the first available SIZE from --block-size, and the DU_BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE and BLOCKSIZE environment variables. Otherwise, units default to 1024 bytes (or 512 if POSIXLY_CORRECT is set). SIZE is an integer and optional unit (example: 10M is 10*1024*1024). Units are K, M, G, T, P, E, Z, Y (powers of 1024) or KB, MB, ... (powers of 1000). GNU coreutils online help: For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'du invocation'6.4 ll命令 执行命令:ll --help,查看详细帮助手册。 Usage: ls [OPTION]... [FILE]... List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default). Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor --sort is specified. Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too. -a, --all do not ignore entries starting with . -A, --almost-all do not list implied . and .. --author with -l, print the author of each file -b, --escape print C-style escapes for nongraphic characters --block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g., '--block-size=M' prints sizes in units of 1,048,576 bytes; see SIZE format below -B, --ignore-backups do not list implied entries ending with ~ -c with -lt: sort by, and show, ctime (time of last modification of file status information); with -l: show ctime and sort by name; otherwise: sort by ctime, newest first -C list entries by columns --color[=WHEN] colorize the output; WHEN can be 'never', 'auto', or 'always' (the default); more info below -d, --directory list directories themselves, not their contents -D, --dired generate output designed for Emacs' dired mode -f do not sort, enable -aU, disable -ls --color -F, --classify append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries --file-type likewise, except do not append '*' --format=WORD across -x, commas -m, horizontal -x, long -l, single-column -1, verbose -l, vertical -C --full-time like -l --time-style=full-iso -g like -l, but do not list owner --group-directories-first group directories before files; can be augmented with a --sort option, but any use of --sort=none (-U) disables grouping -G, --no-group in a long listing, don't print group names -h, --human-readable with -l, print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G) --si likewise, but use powers of 1000 not 1024 -H, --dereference-command-line follow symbolic links listed on the command line --dereference-command-line-symlink-to-dir follow each command line symbolic link that points to a directory --hide=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN (overridden by -a or -A) --indicator-style=WORD append indicator with style WORD to entry names: none (default), slash (-p), file-type (--file-type), classify (-F) -i, --inode print the index number of each file -I, --ignore=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN -k, --kibibytes default to 1024-byte blocks for disk usage -l use a long listing format -L, --dereference when showing file information for a symbolic link, show information for the file the link references rather than for the link itself -m fill width with a comma separated list of entries -n, --numeric-uid-gid like -l, but list numeric user and group IDs -N, --literal print raw entry names (don't treat e.g. control characters specially) -o like -l, but do not list group information -p, --indicator-style=slash append / indicator to directories -q, --hide-control-chars print ? instead of nongraphic characters --show-control-chars show nongraphic characters as-is (the default, unless program is 'ls' and output is a terminal) -Q, --quote-name enclose entry names in double quotes --quoting-style=WORD use quoting style WORD for entry names: literal, locale, shell, shell-always, c, escape -r, --reverse reverse order while sorting -R, --recursive list subdirectories recursively -s, --size print the allocated size of each file, in blocks -S sort by file size --sort=WORD sort by WORD instead of name: none (-U), size (-S), time (-t), version (-v), extension (-X) --time=WORD with -l, show time as WORD instead of default modification time: atime or access or use (-u) ctime or status (-c); also use specified time as sort key if --sort=time --time-style=STYLE with -l, show times using style STYLE: full-iso, long-iso, iso, locale, or +FORMAT; FORMAT is interpreted like in 'date'; if FORMAT is FORMAT1FORMAT2, then FORMAT1 applies to non-recent files and FORMAT2 to recent files; if STYLE is prefixed with 'posix-', STYLE takes effect only outside the POSIX locale -t sort by modification time, newest first -T, --tabsize=COLS assume tab stops at each COLS instead of 8 -u with -lt: sort by, and show, access time; with -l: show access time and sort by name; otherwise: sort by access time -U do not sort; list entries in directory order -v natural sort of (version) numbers within text -w, --width=COLS assume screen width instead of current value -x list entries by lines instead of by columns -X sort alphabetically by entry extension -1 list one file per line SELinux options: --lcontext Display security context. Enable -l. Lines will probably be too wide for most displays. -Z, --context Display security context so it fits on most displays. Displays only mode, user, group, security context and file name. --scontext Display only security context and file name. --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit SIZE is an integer and optional unit (example: 10M is 10*1024*1024). Units are K, M, G, T, P, E, Z, Y (powers of 1024) or KB, MB, ... (powers of 1000). Using color to distinguish file types is disabled both by default and with --color=never. With --color=auto, ls emits color codes only when standard output is connected to a terminal. The LS_COLORS environment variable can change the settings. Use the dircolors command to set it. Exit status: 0 if OK, 1 if minor problems (e.g., cannot access subdirectory), 2 if serious trouble (e.g., cannot access command-line argument). GNU coreutils online help: For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'ls invocation'6.5 ls命令 执行命令:ls --help,查看详细帮助手册。 Usage: ls [OPTION]... [FILE]... List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default). Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor --sort is specified. Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too. -a, --all do not ignore entries starting with . -A, --almost-all do not list implied . and .. --author with -l, print the author of each file -b, --escape print C-style escapes for nongraphic characters --block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g., '--block-size=M' prints sizes in units of 1,048,576 bytes; see SIZE format below -B, --ignore-backups do not list implied entries ending with ~ -c with -lt: sort by, and show, ctime (time of last modification of file status information); with -l: show ctime and sort by name; otherwise: sort by ctime, newest first -C list entries by columns --color[=WHEN] colorize the output; WHEN can be 'never', 'auto', or 'always' (the default); more info below -d, --directory list directories themselves, not their contents -D, --dired generate output designed for Emacs' dired mode -f do not sort, enable -aU, disable -ls --color -F, --classify append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries --file-type likewise, except do not append '*' --format=WORD across -x, commas -m, horizontal -x, long -l, single-column -1, verbose -l, vertical -C --full-time like -l --time-style=full-iso -g like -l, but do not list owner --group-directories-first group directories before files; can be augmented with a --sort option, but any use of --sort=none (-U) disables grouping -G, --no-group in a long listing, don't print group names -h, --human-readable with -l, print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G) --si likewise, but use powers of 1000 not 1024 -H, --dereference-command-line follow symbolic links listed on the command line --dereference-command-line-symlink-to-dir follow each command line symbolic link that points to a directory --hide=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN (overridden by -a or -A) --indicator-style=WORD append indicator with style WORD to entry names: none (default), slash (-p), file-type (--file-type), classify (-F) -i, --inode print the index number of each file -I, --ignore=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN -k, --kibibytes default to 1024-byte blocks for disk usage -l use a long listing format -L, --dereference when showing file information for a symbolic link, show information for the file the link references rather than for the link itself -m fill width with a comma separated list of entries -n, --numeric-uid-gid like -l, but list numeric user and group IDs -N, --literal print raw entry names (don't treat e.g. control characters specially) -o like -l, but do not list group information -p, --indicator-style=slash append / indicator to directories -q, --hide-control-chars print ? instead of nongraphic characters --show-control-chars show nongraphic characters as-is (the default, unless program is 'ls' and output is a terminal) -Q, --quote-name enclose entry names in double quotes --quoting-style=WORD use quoting style WORD for entry names: literal, locale, shell, shell-always, c, escape -r, --reverse reverse order while sorting -R, --recursive list subdirectories recursively -s, --size print the allocated size of each file, in blocks -S sort by file size --sort=WORD sort by WORD instead of name: none (-U), size (-S), time (-t), version (-v), extension (-X) --time=WORD with -l, show time as WORD instead of default modification time: atime or access or use (-u) ctime or status (-c); also use specified time as sort key if --sort=time --time-style=STYLE with -l, show times using style STYLE: full-iso, long-iso, iso, locale, or +FORMAT; FORMAT is interpreted like in 'date'; if FORMAT is FORMAT1FORMAT2, then FORMAT1 applies to non-recent files and FORMAT2 to recent files; if STYLE is prefixed with 'posix-', STYLE takes effect only outside the POSIX locale -t sort by modification time, newest first -T, --tabsize=COLS assume tab stops at each COLS instead of 8 -u with -lt: sort by, and show, access time; with -l: show access time and sort by name; otherwise: sort by access time -U do not sort; list entries in directory order -v natural sort of (version) numbers within text -w, --width=COLS assume screen width instead of current value -x list entries by lines instead of by columns -X sort alphabetically by entry extension -1 list one file per line SELinux options: --lcontext Display security context. Enable -l. Lines will probably be too wide for most displays. -Z, --context Display security context so it fits on most displays. Displays only mode, user, group, security context and file name. --scontext Display only security context and file name. --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit SIZE is an integer and optional unit (example: 10M is 10*1024*1024). Units are K, M, G, T, P, E, Z, Y (powers of 1024) or KB, MB, ... (powers of 1000). Using color to distinguish file types is disabled both by default and with --color=never. With --color=auto, ls emits color codes only when standard output is connected to a terminal. The LS_COLORS environment variable can change the settings. Use the dircolors command to set it. Exit status: 0 if OK, 1 if minor problems (e.g., cannot access subdirectory), 2 if serious trouble (e.g., cannot access command-line argument). GNU coreutils online help: For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'ls invocation'以上,感谢。 2022年11月21日 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |